Keep up with the latest IoT-based building automation, and follow us on LinkedIn!
The manufacturing sector has long been the backbone of global economic development, but it’s frequently associated with high levels of pollution, wastage, and environmental degradation. The manufacturing industry must be mindful of resource utilisation and wastage in a highly competitive and dynamic global market with stringent environmental regulations.
“20% of every dollar spent in the manufacturing industry is wasted – adding up to $8 Trillion, or 10% of the GWP” – Forbes
This 20% waste is not the physical waste produced by the manufacturing process, rather it’s the economic waste, i.e., money & resources spent because of inefficiencies and negligence that didn’t have to be.
Three major types of utilities or resources aid in the operation of a typical manufacturing plant: electricity, water, and gas.These critical resources are, for the most part, non-renewable, so their production has a significant negative impact on the environment. Another obvious fact is that these resources, particularly electricity and gas, are not cheap, so unnecessary waste should be avoided at all costs.
Challenges in a typical Manufacturing setup
In a manufacturing setting, common challenges include lack of visibility & manual utility management, which lead to unmonitored resource utilization, and hence, unnecessary wastage. Today, when we’re constantly talking about industry 4.0, manual readings from energy, gas, and water meters are still prevalent, resulting in a lot of paperwork and, ultimately, operational inefficiencies.
1. Manual Utility Management
“Manual utility management” is one of the most prominent challenges in the manufacturing industry. Even today, when almost everything is smart and automated, manual reporting of utilities (Energy, Water & Gas) remains a challenge in manufacturing plants. Such manual efforts are prone to errors as they are carried out by humans, who eventually face fatigue and lose focus, among other limitations. When such errors occur repeatedly, they can lead to larger problems. It has already been proven in the history of economic development that redundant tasks are better performed by technology, i.e., automation.
2. Lack of Centralized Visibility
Most manufacturers can only monitor aggregated energy consumption and lack real-time visibility at the plant and machine levels. Furthermore, there’s limited to no visibility into the performance of mission-critical assets & machines. Access to energy and performance information and the ability to effectively analyze such real-time data is vital for successful energy and asset management.
3. Sudden Asset Breakdowns
Asset breakdowns occur when machinery is prolonged working without regular maintenance resulting in disrupting the plant operations. It happens due to a lack of centralized visibility into asset health.Electrical hazards also disrupt the processes because of current & voltage imbalances. Therefore, real-time monitoring & automated alerts are imperative for seamless operation of a manufacturing plant.
Such issues must be addressed in order to improve operational & utility efficiencies.
IoT Applications in Manufacturing: Taking the challenges head on!
IoT-powered Utilities & Critical Asset Management solutions are taking on the challenges in the manufacturing space. From automated readings & alerts to machine energy benchmarking & predictive maintenance, IoT provides the manufacturing sector with the systems and tools it needs to improve the centralized monitoring of utilities and various machines. It provides centralized visibility at the plant and asset levels, allowing for better resource utilization and operational optimization.
Benefits of IoT powered Automation in Manufacturing Plants
1. Automated & Real-time Utilities Monitoring
IoT-powered utility management completely automates the data collection process in real-time. Energy meters, water flow meters, and gas flow meters are installed to collect critical data. Such data is then transmitted to the cloud and presented as actionable insights to the plant heads & maintenance team via a web-based dashboard.
IoT-powered energy meters monitor electricity incomers like Grid, DG, Solar, etc. and consumption by plant assets & equipment. This type of intelligent monitoring provides real-time visibility into critical parameters such as energy consumption, run hours, power factor, current and voltage health.
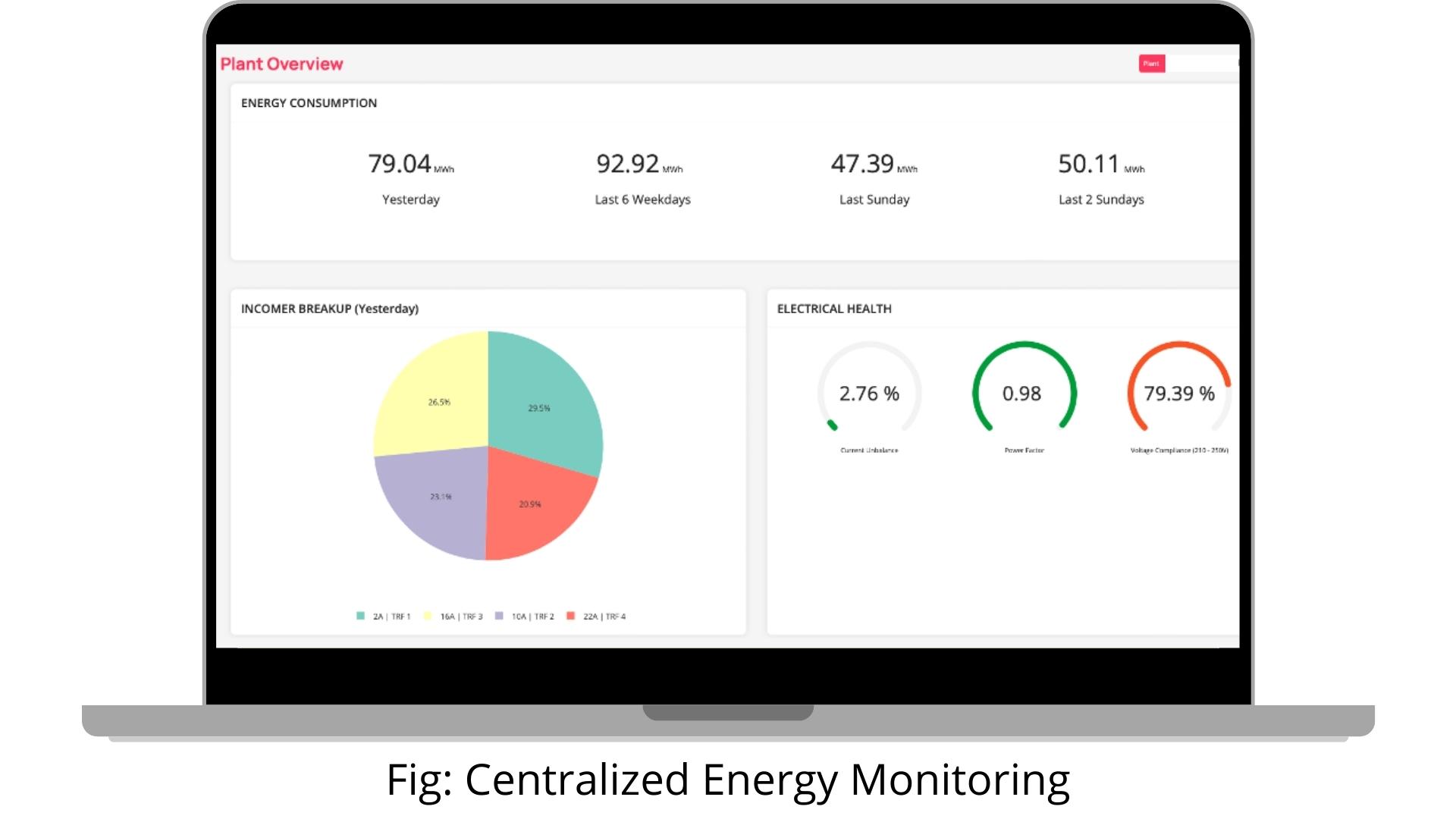
Similarly, Water Flow and Gas Flow meters track real-time water and gas consumption, eliminating the need for manual recording of readings and excess paperwork while increasing operational efficiencies.
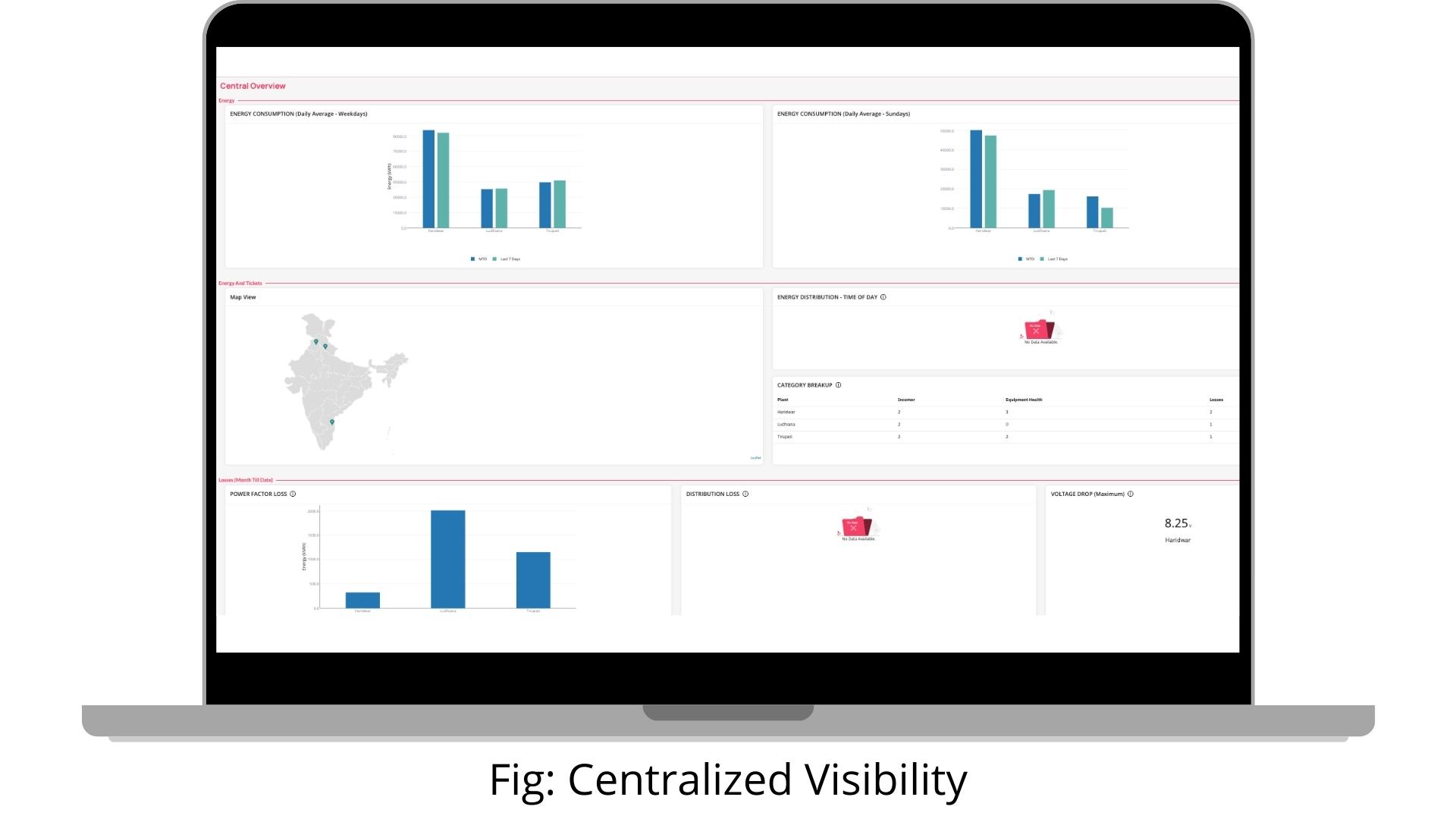
 2. Centralized Visibility
2. Centralized Visibility
IoT powered Utilities & Critical Asset Management solution offers advanced data analytics & representation. Such processed data is then delivered to stakeholders as critical actionable insights on their personal devices, such as laptops or smartphones. As a result, the entire system can be accessed from anywhere in the world using role-based access control, allowing for seamless centralized monitoring and control.
3. Automated Anomaly Detection & Ticketing
IoT enables proactive maintenance of plant assets and equipment, reducing the likelihood of them failing entirely in the first place. Predictive maintenance forecasts when a piece of equipment will need maintenance to avoid unexpected equipment failure. It’s based on parameters that monitor the actual condition of assets, rather than a time-based or reactive approach. It uses energy meters to analyze voltage unbalance, power factor, and other parameters to detect anomalies. In the event of any anomaly, the maintenance team is notified via an automated ticketing system for immediate resolution.
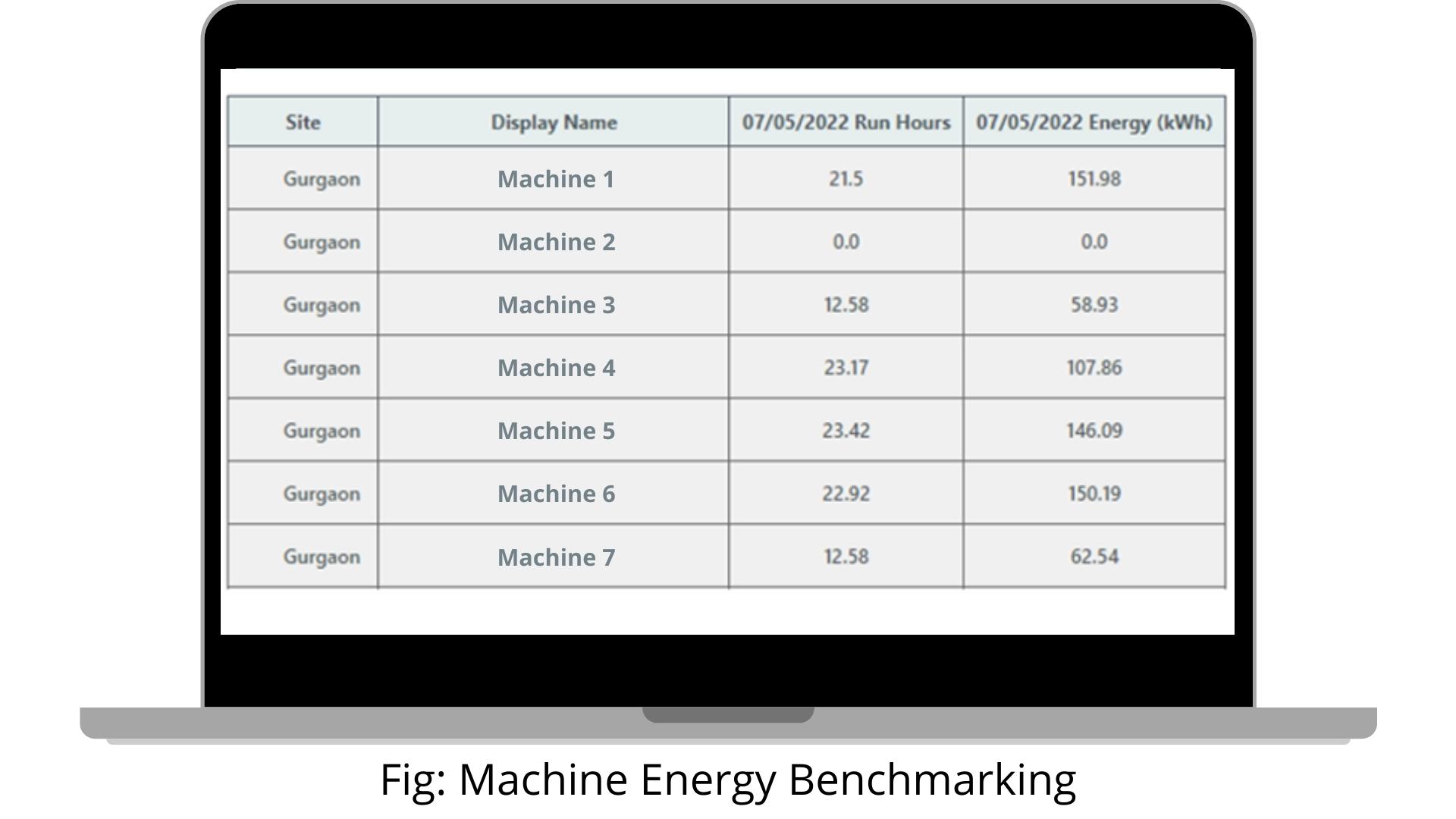
4. Energy Benchmarking
The energy benchmarking process evaluates machinery’s energy consumption and compares it to the performance of similar machinery or a predefined standard. Energy benchmarking powered by IoT is the most effective method for tracking the energy efficiency of machinery over time. It’s a critical component of industrial energy management. Energy benchmarking makes it simple to identify inefficient machines, make decisions about potential improvements, and make informed long-term energy management decisions.
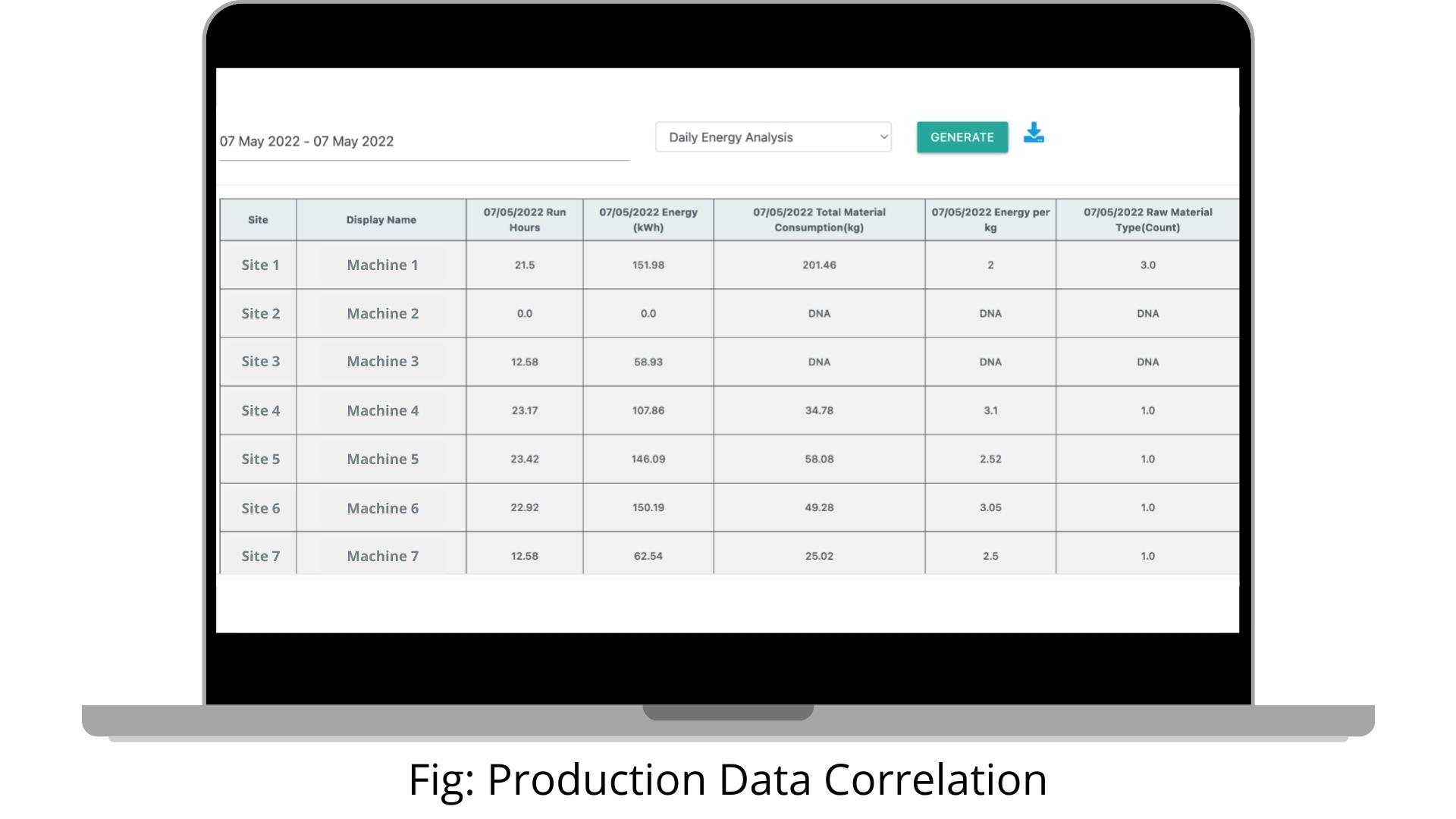
5. Production Data Correlation
External business metric integration allows for identification of energy consumed per unit of raw material consumed per machine. This level of visibility and analysis enables data-driven decision making for better resource allocation and optimization.
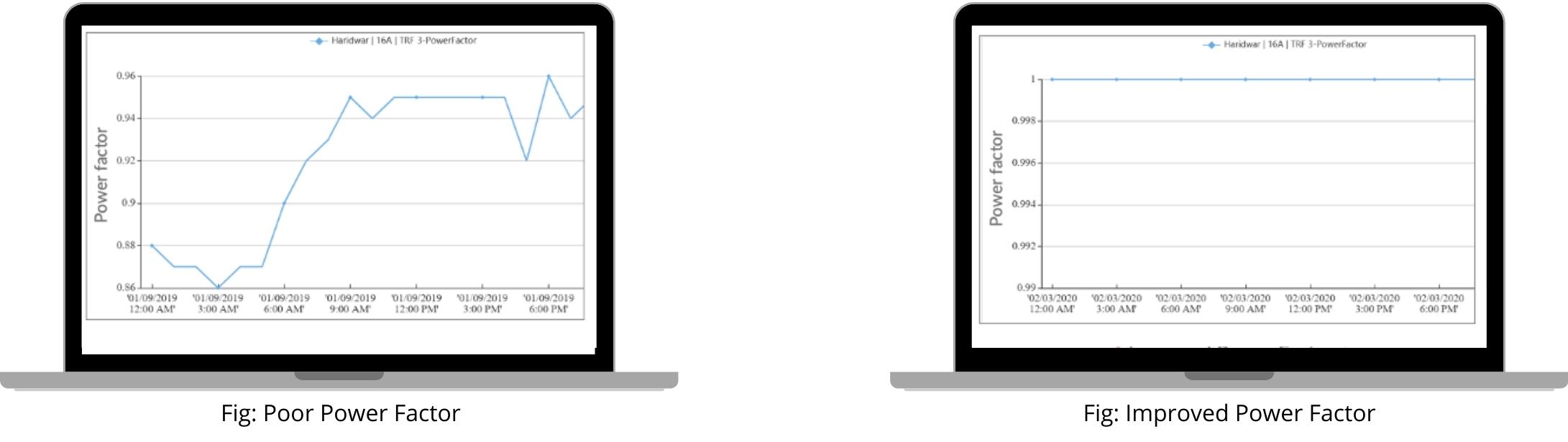
6. Electrical Safety Compliance
Smart IoT energy meters continuously monitor electrical parameters such as power factor, current and voltage statistics and send alerts if any irregularities are detected. The appropriate team can then take corrective action to avoid serious consequences such as equipment/component failure and penalties in the event of a low power factor.
 Benefits of IoT in Manufacturing
Benefits of IoT in Manufacturing
1. Overall Resources Efficiency & Optimization
IoT-powered Utilities & Critical Asset Management solutions give facility managers complete visibility into plant operations. Cloud-based analytics enable such visibility and anomaly detection in case of utility wastage, such as energy leakages caused by asset inefficiencies or simply running when not needed, water leakages, etc. Furthermore, it enables intelligent automation & control, which can save energy by directly controlling certain systems, such as cooling, lighting, etc., and even specific plant sections.
2. Improved Asset Health & Performance
FDD or fault detection & diagnosis keep a close eye on asset & machine health and performance. In case of any abnormality or irregularity, the maintenance staff is notified via an automated ticketing system for immediate rectification. Such proactive maintenance improves assets’ overall performance and health, resulting in a higher return on asset investment.
3. Reduction in Sudden Equipment Breakdown
Predictive maintenance employs IoT sensors to monitor parameters such voltage & current unbalance, power factor, and so on to detect early faults. It’s a very effective technique as it results in smooth operations with no sudden surprises and overall cost savings for the company.
4. Reduction in Electrical Penalties
A poor power factor, i.e., low power factor, draws more current than a load with a high-power factor for the same amount of useful power transferred. This results in higher load current and hence higher losses. Therefore, it’s always desirable to have a near-unity power factor. If not, this low power factor results in inefficient energy consumption, resulting in significant penalties on the electricity bill. Continuous automated monitoring of power factor provides visibility and aids in avoiding such severe penalties.
The challenges in the manufacturing sector, which typically revolve around lack of visibility and manual utilities management, can be countered by ZenConnect, IoT powered Utilities & Critical Asset Management solution for the industrial sector. It’s an enterprise IoT solution that offers detailed energy monitoring & optimization, visibility into machine health, and ensures electrical health & safety.
See how ZenConnect helped a leading auto component manufacturer meet its automation and energy-saving goals and reduce unplanned machine breakdowns by 20%. Download the case study.
Keep up with the latest IoT-based building automation, and follow us on LinkedIn!

